The Similarity matrix displays data showing the
similarity between two variables. We are able to identify the similarities in
the matrix by the varying colors used in the matrix. The above matrix shows
similarities between image text description for a software..
Tuesday, July 16, 2013
Correlation matrix
A Correlation matrix displays the correlation
between the different varieties of variables. When the same variables are
compared in the matrix the value/coefficient is always one. In the correlation
matrix above there are eight different variables shown and eight correlation
coefficients.
Star plots
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Radar_chart
In a star plot there can be multiple variables
being compared. A star is formed when the lines from the variables connect
creating a star shape. The above is an example of a star plot used by NASA to compare
different design results. They are testing each design for accuracy, collision,
time, mass, link defection, trajectory completion, and actuator saturation. The
center of the star plot represents the most desired results, which in this case
is the MER IDD and is represented by the red line.
Stem and Leaf plot
http://www.eduplace.com/math/mhm/5/06a/
A Stem and Leaf plot is a statistical plot that
displays quantitative data. For the stem and leaf plot above it shows the ages
of people at a family reunion. The data for this stem and leaf plot was split
into a left column, stem, and a right column, leaf. For these types of plots
there is always one stem and can be multiple and repeating leafs. An example of
what the numbers look like before they are divided into a stem and leaf plot
are 32, 45, and 81.
Box plot
http://www.itl.nist.gov/div898/handbook/eda/section3/boxplot.htm
A box plot graph shows numerical data for
different variables on an x and y axis. The lines extending outside of the
upper and lower part of the box plot are called whiskers and they represent
variability outside of the box plot. In the box plot above the x axis
represents the comparison of four machines for energy output and the y axis
represents the energy response. From the information provided above machine
three has the highest energy response, machine two the second, machine one the
third highest and machine four has the least energy response.
Histogram
A histogram is represented by a bar graph and can
display one or more variables on a graph, these graphs are also known as
frequency distribution graphs. These types of graphs shows the distribution of continuous
data which is represented on an x and y axis, also the bars should always be
next to each other when displaying the information. In the histogram above a
single variable is represented, the scores on the final exam and the y axis
represents the number of students which ranges from 0-50 and the x axis
represents the score on final exam which ranges from 0-100. This graph also
uses different colors to represent the different scores which I found made it
easier to read.
Parallel coordinate graph
A Parallel coordinate graph represents two
or more variables. The above displays information on an x and y axis. The y
axis represents greenhouse gas global warming potential from lowest,
represented using red lines, and highest, represented using purple lines. The x
axis displays 6 different software implementation versions and each are separated
by a black line that runs vertical through the graph. I find these types
of graphs to be difficult and hard to read.
Triangular plot
A triangular plot represents three variables. In
the triangular plot above the three variables that are being represented are
clay, silt, and sand. The numbers that run along the triangle represent the
percentage for each variable. In the example above it shows that a sandy loam has 10% clay, 60% sand, and 30% silt.
Windrose
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wind_rose
A windrose is a graph tool that is commonly used
by meteorologist to graph wind speed, and its direction for a specific
location. The windrose measures the frequency of wind blowing from a certain
direction over time. Each spoke that is represented above displays the wind
speed for LaGuardia Airport in 2008. This graph shows the wind direction that
had the greatest frequency was the Southern direction.
Climograph
A climograph is a graphical representation of precipitation
and climate temperatures for a certain area. These graphs are easy to read
since they display only two types of information for one specific area. In the
above climograph it is displaying the temperature and precipitation in a 12
month period for Calcutta. If someone wanted to go back to a specific year and
month to look at the temperature they would be able to easily do this. It is
easy to read and understand these types of graphs, the above shows that
participation is represented by the green bars and temperature is represented
using the red line.
Population Profile
A Population Profile shows
two variables, men and women on a bar chart that displays them as a function
for their age group. The x axis represents the population and the y axis
represents the age in years for this map. This map is measuring the males and
females with and without AIDS.
Scatterplot
http://www.netmba.com/statistics/plot/scatter/
A scatter plot uses two variables for a set of
data. Each point represents the two variables, one from the x axis and the
other from the y axis. The scatter plot can show correlations between the two variables.
The two variables in the scatter plot shown above are response variables and
explanatory variables.
Index value plot
An Index value plot measures the index value between one or
more variables. These types of maps are commonly used in the stock market. The
above graph shows one variable being measured, Raw ARMS Index for 2004.
Accumulative line graph or Lorenz curve
Accumulative line graph or Lorenz Curve shows the
degree of inequality between two variables (A & B). These types of lines graphs
are often used to represent income distribution between the two variables. The
above Lorenz curve shows the distribution amongst people with the lowest to
highest incomes.
Bilateral graph
http://www.gallup.com/poll/106858/chinas-leadership-better-regarded-outside-west.aspx
Bilateral graphs display two or more sets of data
on a single graph and can be represented as line or bar graph. The above graph
displays three different sets of data, approve, disapprove and don't
know/refused. The information is determining whether people approve or disapprove
of the job performance of the leadership of china.
Nominal area choropleth map
Nominal area choropleth maps use nominal data, which means that colors or symbols may be used to differentiate a phenomenon in either a
certain area or region. The above map displays nominal data by using different
colors and shades to represent the leads and wins for the Democratic and
Republican Parties in each state.
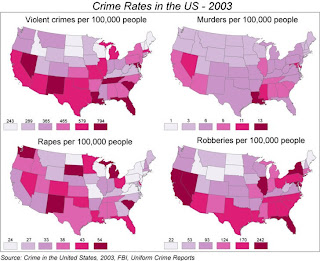
Unstandardized choropleth map
An unstandardized choropleth map uses data with raw sets
of numbers. Different colors are used to differentiate between the numbers used
in the map. The above is an example of an unstandardized choropleth map; four
different types of crimes reported in the US for 2003 are shown by using different
colors to represent a set of raw numbers that represent people who committed the
crime.
Standardized choropleth map
Standardized choropleth maps show areally
averaged data that is represented within one area or unit of the map. A common
use for these types of maps is to show population per square mile. The above
map is an example of this showing the population density per square mile.
Univariate choropleth map
A univariate choropleth map displays data for only one
variable. To differentiate between the categories different shades of the same color
are used. The above map represents the percentage of individuals living in
poverty by county for 2000.
Bivariate choropleth map
http://www.geo.unizh.ch/~annal/Choropleth%20maps.html
A Bivariate choropleth map uses 2 variables to
display information on one map. To differentiate between the 2 variables
symbols or colors can be used to show the different relationships of phenomenon
in the map. The above map shows 2 variables of information being displayed in
the map using colors. The blue shades represent the percentage of rural
populations and the red colors represent percentage of population under the age
of 18. The map then takes the separate information and places it into a larger
map where you can see how the two phenomenons differentiate.
Unclassed choropleth map
Unclassed choropleth maps differ from classed
choropleth maps because there are no set intervals and they are characterized
by color intensity. Different color shades are used to represent different
values on the map. Depending on how many values there are in the map will
determine how easy or difficult it is to read or understand. Too many values, the
colors will start to blend and make it hard to differentiate.
Classed choropleth maps
http://my.ilstu.edu/~jrcarter/Geo204/Choro/Tom/
A classed choropleth map differs from an
unclassed choropleth map by combining areal units into a smaller number of
groups. Interval levels may vary, but typically 4 to 7 are used in a map.
There is different classification techniques used to divide up the intervals.
An example of the different classification techniques used is equal steps,
quantities, natural breaks, and minimum variance. The above map shows the
percentage of Hispanics per county in Florida and uses 5 natural breaks.
Range graded proportional circle map
A Range Graded Proportional Circle Map is a
proportional circle map that uses circles in relation to the different range of
data. For these maps each circle size represents a set of numbers that has a different
range of values. The above map shows motor vehicle deaths in different areas.
Continuously variable proportional circle map
A continuously variable proportional circle map is a
variation of a proportional circle map. How a continuously variable
proportional circle map differs from a proportional circle map is that
multiple variables are being represented. In the example above it shows the
different types of meat that was sent to Paris butcheries from different
regions in France.
DOQQ
DOQQ refers to Digital Orthographic Quarter-Quads and are
produced by the USGS. These types of maps combine image characteristics that
were taken from an aerial photograph. The DOQQ is an aerial photo that has been
taken and orthorectified, a technique that removes distortion out of the aerial
photo so that it can be used as a flat map. The DOQQ image above shows part of
a Farmville in North Carolina.
DEM
http://vro.dpi.vic.gov.au/dpi/vro/vrosite.nsf/pages/digital_elevation_models
DEM refers to digital elevation models. The DEM
is a digital image that consists of terrain elevation data and is represented
in either a 3-D image or a digital model of the Earth’s surface. The images may
be colorized to bring out relief of the surface. The above is an image using
DEM to show the difference in elevation across the Earth surface.
DLG
http://web.wt.net/daba/dlg/default.html
DLG stands for digital line graph and is
represented through digital vector form. These types of graphs can be used to
display a variety of information such as roads, boundaries and utility lines.
The above DLG displays important culture data for lakes and streams.
DRG
http://egsc.usgs.gov/isb/pubs/factsheets/fs08801.html
DRG stands for Digital Raster Graphics and is a
scanned georectified U.S. Geological Survey topographic map. These types of
maps are offered to the public and provide the same information as a paper map.
This DRG image shows a river running through the district of Colombia.
LIDAR
https://www.saic.com/geospatial/modeling/lidar-urban-modeling.html
LIDAR refers to light detection and ranging. It
is another form of remote sensing that uses a laser to pick up images of both
natural and manmade structures. The above is a photo using a LIDAR image by
SAIC, an urban modeling system. With the LIDAR image they are able to plan
upcoming projects and mission planning for emergency response.
Black & white aerial photo
http://isaacalongi.com/kansas-city-aerial-photography/
Black and white aerial photos are a form of
remote sensing that is taken from a satellite, airplane, or space. The image
that is being captured takes place in the biosphere, atmosphere, and
lithosphere. In the image above a black and white photo is taken of Kansas.
Infrared aerial photo
http://www.stocktoninfrared.com/aerial-infrared-roof-moisture-surveys/
Infrared aerial photos are a remote sensing technique that
takes an image using a satellite, airplane, or something from above. Infrared
emulsions differ from black and white emulsions because it is sensitive to
wavelengths that fall outside the range of human vision. IR imagery uses false
color and is able to track temperatures to monitor certain issues or
conditions. In the example above the infrared aerial photo shows moisture
levels on roof tops. This can be useful for detecting future water damage and
safety hazards on homes.
Cartographic animations
Cartographic animation mapping is created
through computers or video. This type of mapping is used for displaying change
over time. The above image shows the changing imagery of Hurricane Katrina as
it moves towards inland. This is a useful visualization so that we get a
general idea of how bug the storm is, whether it is still developing or diminishing
before it hits land.
Statistical maps
http://www3.uakron.edu/src/DataServ/Abstract/
Statistical maps are used to convey a variation
in quantity. These maps can be used for rainfall, population, or for the map
above, workers who commute to work by private car and drive alone. The information
is represented by providing the number or value that it represents.
Cartograms
http://amphibiaweb.org/amphibian/cartograms/
Cartogram maps distort space in order to convey information
of an alternative variable. These types of maps turn thematic mapping variables
such as population or travel time into a value for land distance or area. Distance
and area are the two main types of cartograms. The above map shows the
percentages of threatened and endangered species by country. The different
shades of red are used to represent different percentage ranges.
Flow maps
Flow maps are used to convey the flow path across a surface
and the intensity of the flow. These maps will show the general direction and
not the actual path. Flow maps can be used for traffic flow, social network,
exchange of goods and services between locations, and in this case migration
flow. In the map above the red indicates the south flow and the blue indicates
the north flow and the yellow surrounding the flow represents noise sensitive
areas.
Isoline maps
Isoline maps are lines that connect points of
equal value. They can be used on graphs, charts, and other maps that want to
show areas that have equal value. In the isoline map above it is connecting
areas in the United States that have equal value. The lines can be used to
connect equal value of rainfall, air pressure, or temperature.
Proportional circle map
Unlike dot maps, Proportional circle maps are made with a
circle. The different sizes of the circles are used to measure variable not
necessarily the area over which is being measured. These maps can be useful
when needed to show large amounts of data in different areas. The above map
shows the number of people killed in road accidents in Europe for the year
2000.
Choropleth Map
Choropleth maps are maps that that portray areal
data. The areal data is divided into boundaries for states and/or countries.
Areally averaged information for choropleth maps is done by using either
density per square mile or percentages on a scale of 0-100. In the choropleth
map above is it showing unemployment rates in the country for each state. They
are using percentages and each shade of blue represents a different percentage
range of unemployment. This map could be beneficial for someone looking to move
and is concered about finding a job.
Dot Distribution Map
In dot distribution maps, each dot represents a certain
number. In the dot map above each dot equals 100,000 people living in a certain
area. Dot maps visibly show the scatter of phenomenon based on what is being
represented. It can be differentiated by the different shapes of the dots or
colors used to represent the themes, in this example the dots are blue.
Examples of information that dot maps can convey are township population,
population of a state, or health issues.
Monday, July 15, 2013
Doppler Radar
The Doppler Radar uses the Doppler effect to measure velocity
at a distance using microwave signals for a specific location. It is commonly
used to make atmospheric profiles of clouds, which it does by using the
microwave signals. Doppler radar is able to keep track of the change in movement
of clouds, and precipitation which makes it useful to track storms. The above
shows the Doppler tracking a storm over a certain area.
Isopleths
Isopleths
maps are contour lines that show a phenomenon in specific areas. These maps
convey information by connecting points of equal ratio. The above shows total water
from a storm throughout different areas.
Isopach
http://www.geo.utexas.edu/faculty/barker/kempter/rbtephra.html
Isopach maps use contour lines to represent thickness over a specific area. The above is an example of an eruption of the Rio Blanco tephra. The tephra is an airfall deposit that ranges in thickness. This map uses a symbol, + , to indicate where the airfall is the thickness over the specific area.
Isopach maps use contour lines to represent thickness over a specific area. The above is an example of an eruption of the Rio Blanco tephra. The tephra is an airfall deposit that ranges in thickness. This map uses a symbol, + , to indicate where the airfall is the thickness over the specific area.
Isohyets
http://www.info.bw/~mettest/bulletins/data/bulletin_0210/bulletin_0210.html
Isohyets are lines that connect equal amount of rainfall in different regions. In the above example it shows three different regions and the blue line is used to connect the regions that are experiencing the same amount of rainfall for the given period.
Isohyets are lines that connect equal amount of rainfall in different regions. In the above example it shows three different regions and the blue line is used to connect the regions that are experiencing the same amount of rainfall for the given period.
Isotachs
Isobars
http://www.weatheronline.co.uk/reports/wxfacts/Isobars-on-surface-maps.htm
Isobars are lines that are drawn on weather maps that connect equal lines of pressure.In the example above you can see a red line that connects pressures at 1020 and indicates it at high. There is another line that connects 1010 and is represented using a blue line to indicate low pressure. This maps it easy for someone to look at and easily read the high and low pressures that are connected using lines.
Isobars are lines that are drawn on weather maps that connect equal lines of pressure.In the example above you can see a red line that connects pressures at 1020 and indicates it at high. There is another line that connects 1010 and is represented using a blue line to indicate low pressure. This maps it easy for someone to look at and easily read the high and low pressures that are connected using lines.
Propaganda Map
A propaganda map is a map that uses art or images to persuade
or get a point across to an audience. These maps are false and used primarily
for persuasion. Propaganda maps were commonly used during war to show political
issues. These types of maps have the tendency to be racial, political and/or
glorifying an area. The above shows a propaganda map referring to
the world according to the USA.
Hypsometric Maps
Hypsometric maps are three dimensional surface
maps. These maps are used to show different elevations of the earth by using
color, shading, tinting, and contouring. In the map above it shows raised relief
by displaying the different elevation starting from sea level. The dark blue
shows the depth of the ocean and the contrast of light blue shows the elevation
rising. The same goes for the shading of the greens and browns. By looking at
this map you are able to recognize the ocean, land, and mountain that are being
represented in this hypsometric map.
PLSS maps
The PLLS divides domains that are owned by the Federal Government. The PLLS divides the land up in 6-mile square townships that go north, south, east , and west which run along the meridian and baseline. The baseline indicates north and south whereas the median indicates east and west.
Cadastral Map
A cadastral map is a map that is used to show
real property of a country. In these maps one can show ownership of land by metes and bounds. These
maps are important for public records to show ownership of that specific
property. The above cadastral map shows the boundaries of a neighborhood. This could come in handy if someone wanted to add a fence to their property. They would be able to refer to public records to see the exact coordinates of property they own so they know where to place the fence.
Thematic Maps
http://www.gigawiz.com/thematic.html
A thematic map will focus on spatial
distributions of phenomenon for a theme that will show results for different locations.
An example of different themes that these maps can convey are political,
racial, population, health concerns such as AIDS or HCV, age groups and
rainfall. These maps will always include specific information so that they are
easy to read and follow. In the thematic map above it shows the United States
and each state boundary that favors the Republican or Democratic Party. This
particular map is easy to identify, the two colors used to label between the political
parties and the areas that favor a particular party over the other are easy to
identify and see. Whatever the theme may be it will use different colors to
represent the theme and also visible boundaries to show specific information
for that area.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)